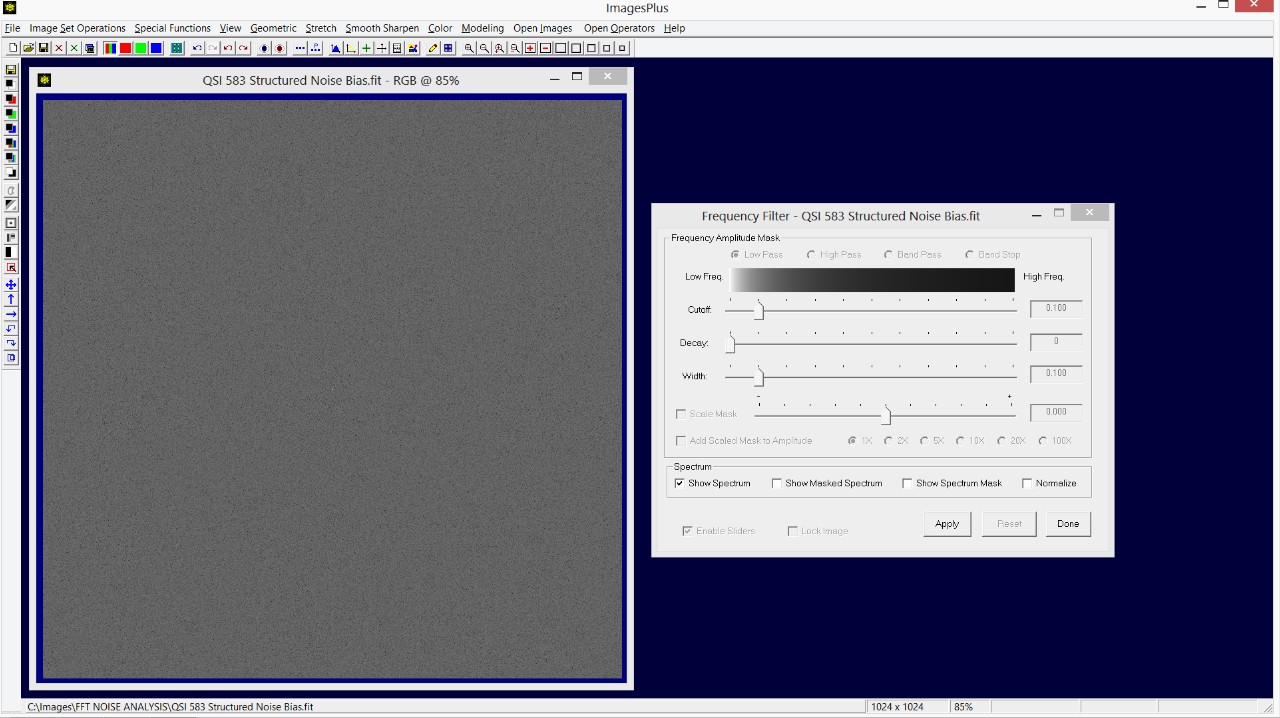
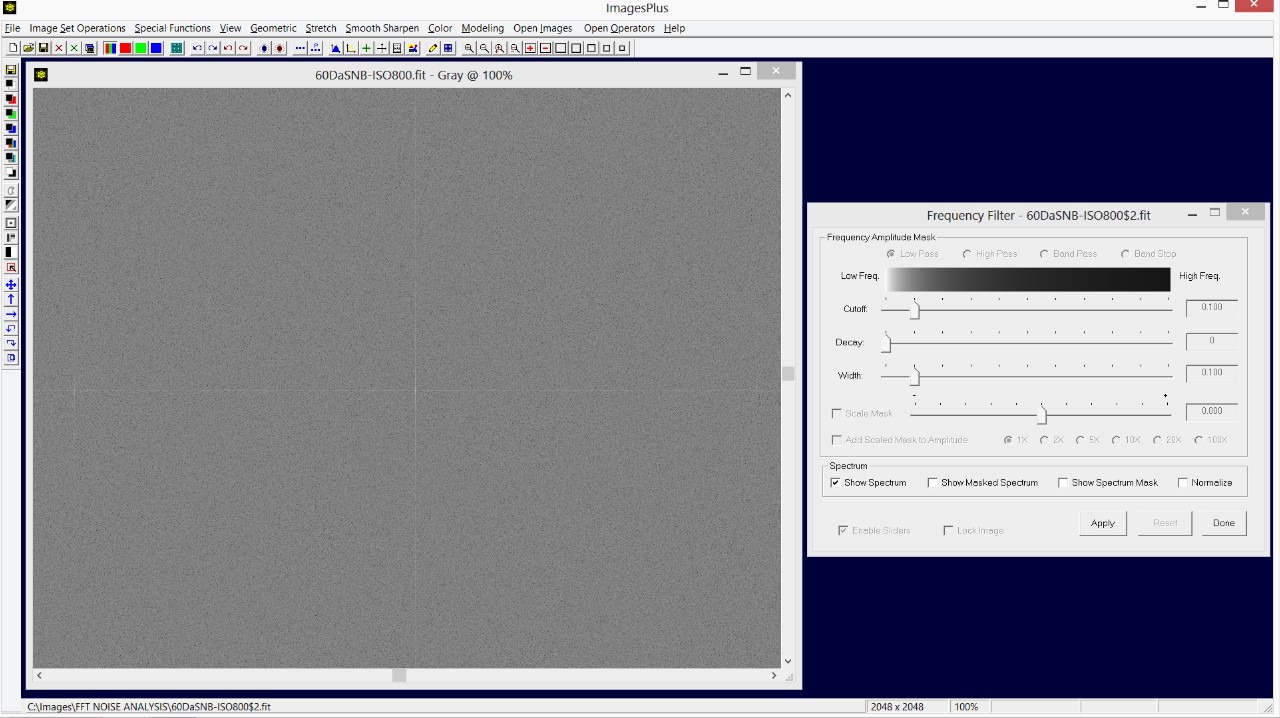
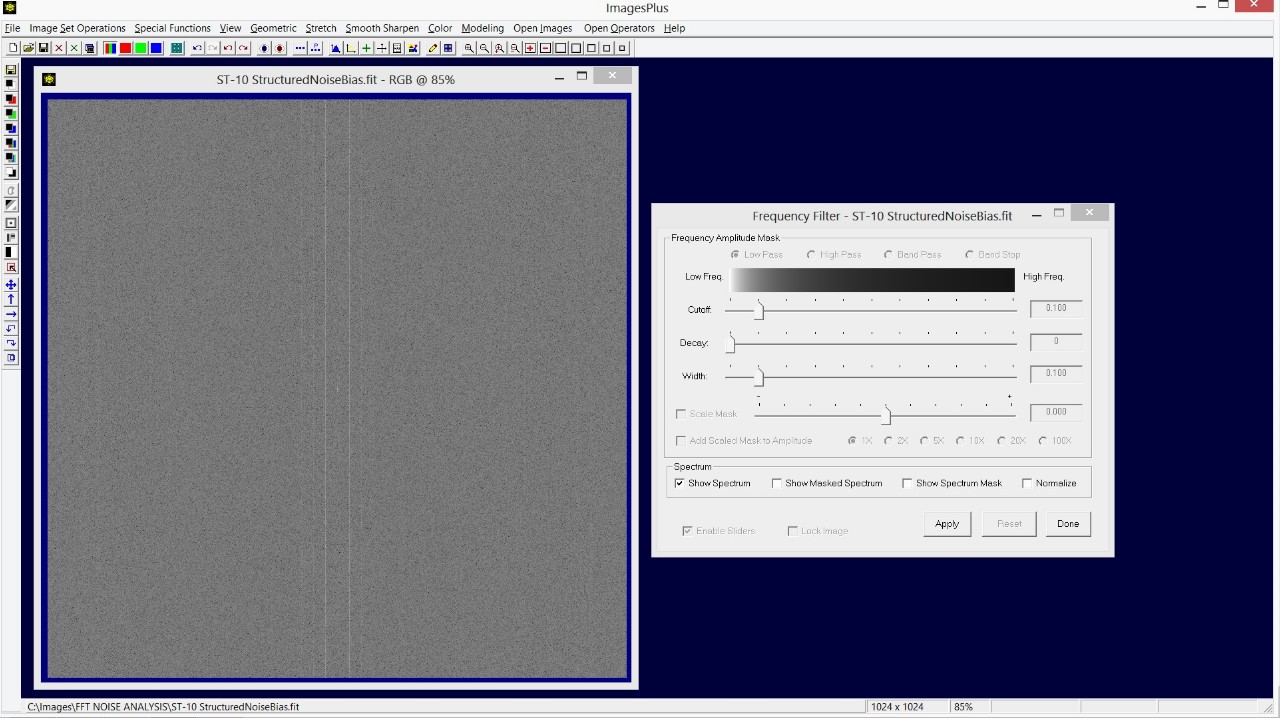
- Use the Smooth Sharpen | Frequency Filter tool to check for structured noise in the calibrated, stacked, and stretched image.
The calibrated, stacked, and digital development stretched image is shown on the left. On the right is a duplicate of the image with the Frequency Filter applied with the Show Spectrum option. Note the fine horizontal and vertical lines that match the structured noise bias frame shown in the previous screen shot.
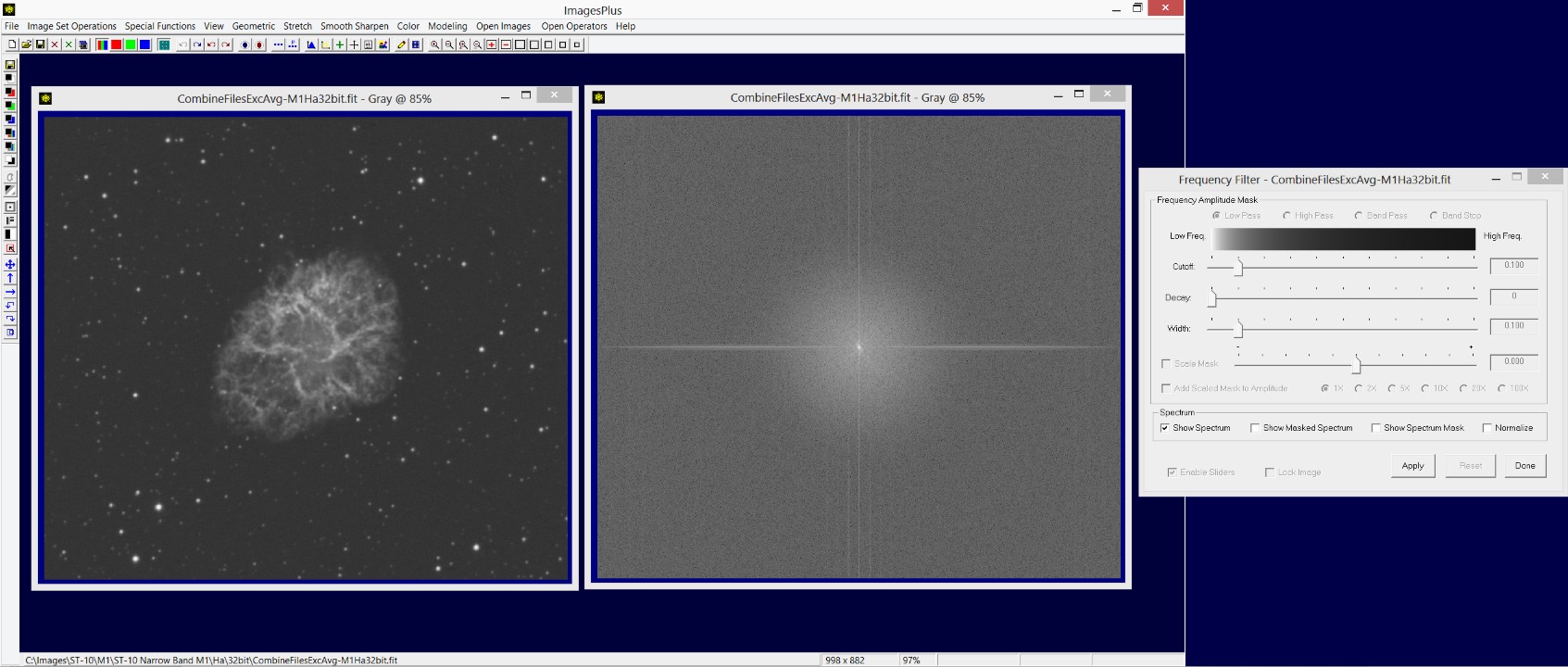 |
- Use the Smooth Sharpen | Split Frequency tool to create a frequency spectrum that can be painted on to remove unwanted frequencies.
Open the Smooth Sharpen | Split Frequency tool. The default setting will create a frequency spectrum and an update image that is the modified version of the initial image using the modified spectrum. The Smooth Sharpen | Combine Frequency tool will be opened automatically and setup with the initial M1 image, spectrum, and updated M1 combination image as shown by the next screen shot.
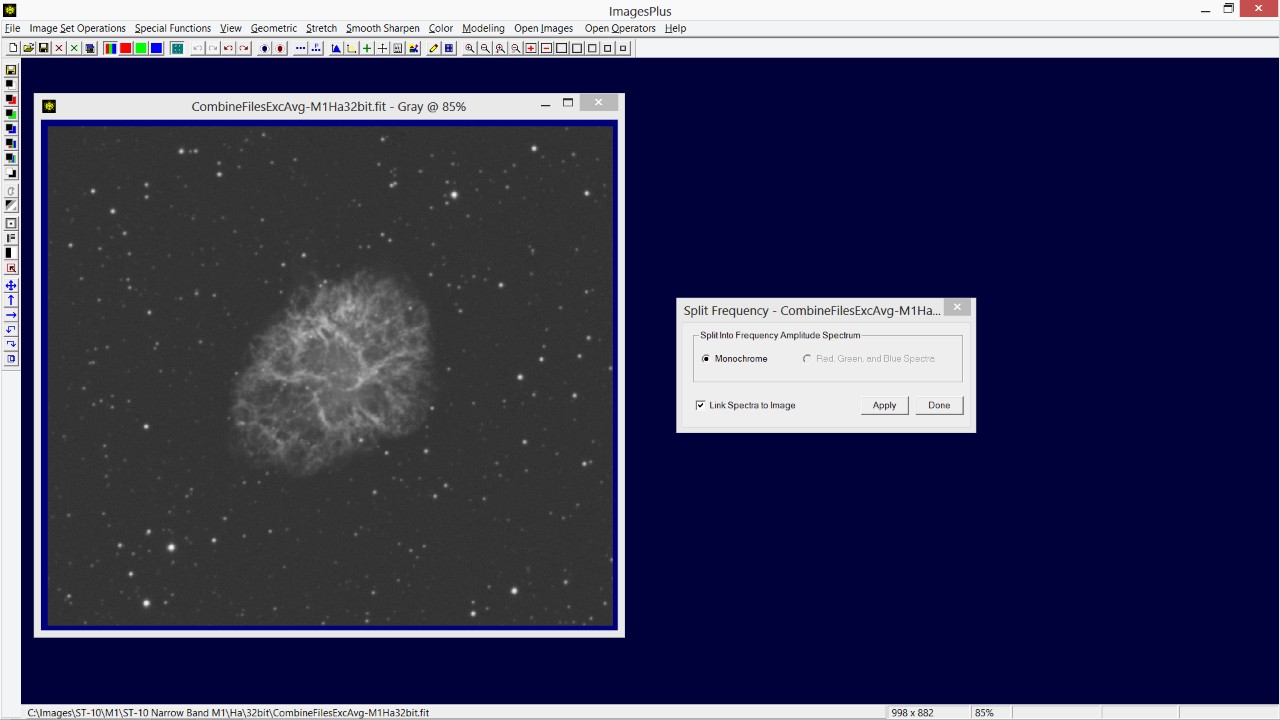 |
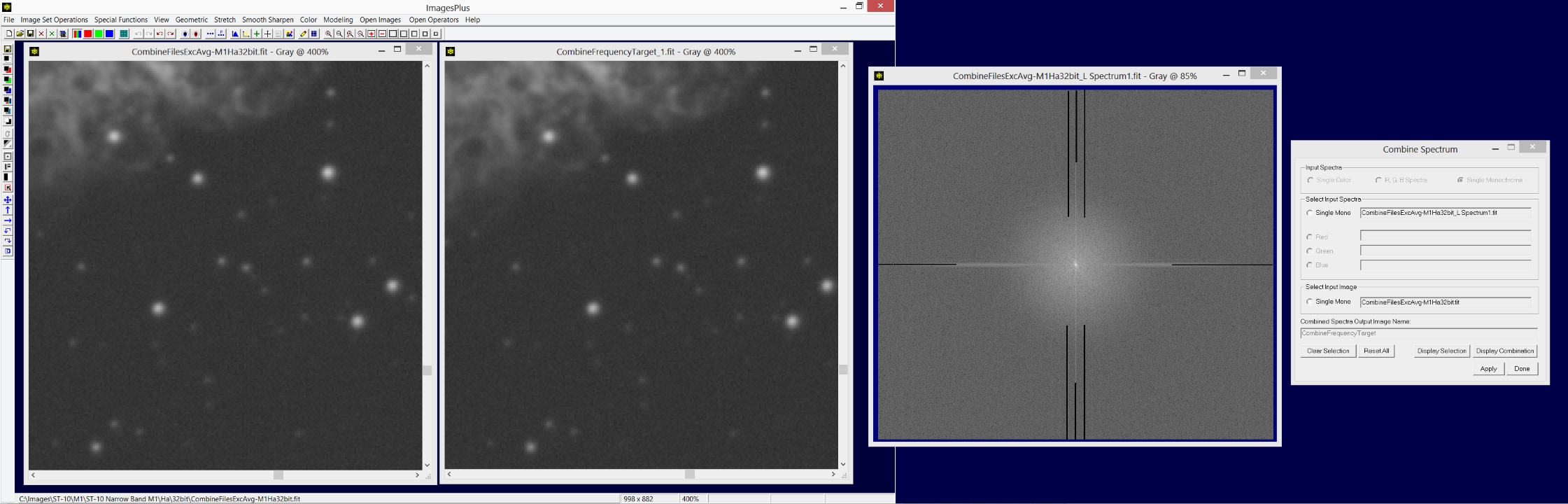
M1 image is shown on the left. M1 updated image at the center and its initial spectrum image on the right. The Combine Spectrum tool is shown on the far right.
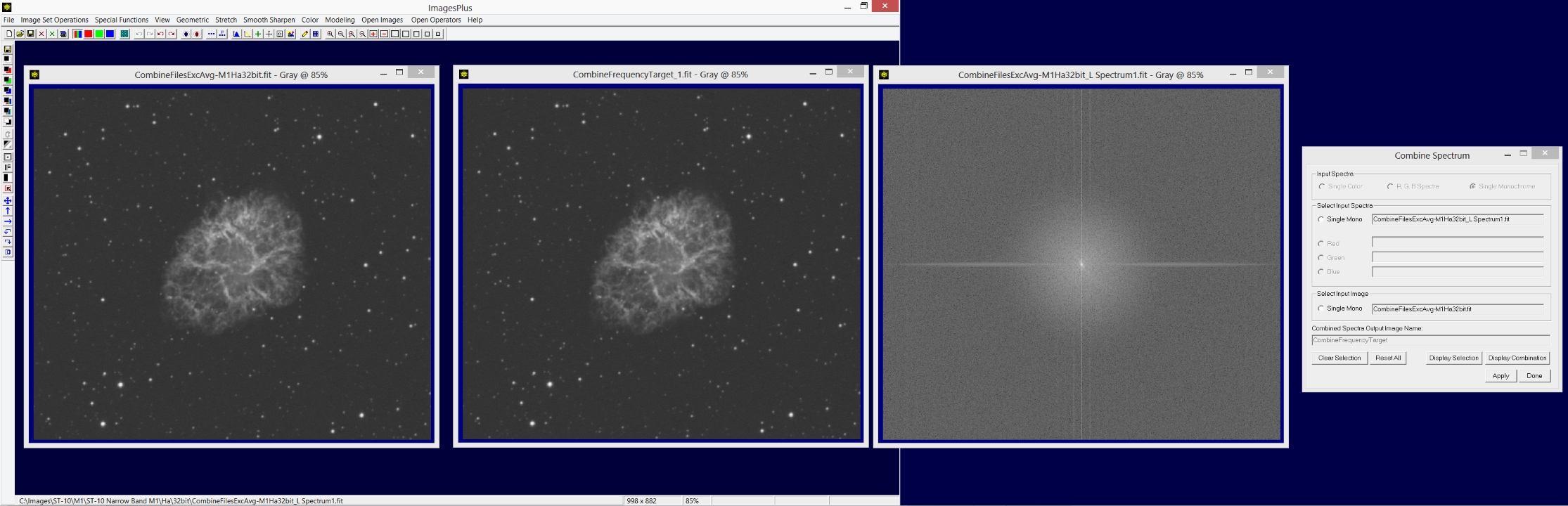 |
Open the Local Smooth, Sharpen, and Paint tool from the left vertical toolbar. Use the Horizontal Line Fill and Vertical Line Fill options with Intensity = 0 or black to paint out the fine vertical and horizontal lines on the spectrum as shown above. Only paint with 0 on the spectrum to eliminated the vertical and horizontal line frequencies. Press the Apply button on Combine Frequency to update the combination image using the painted spectrum.
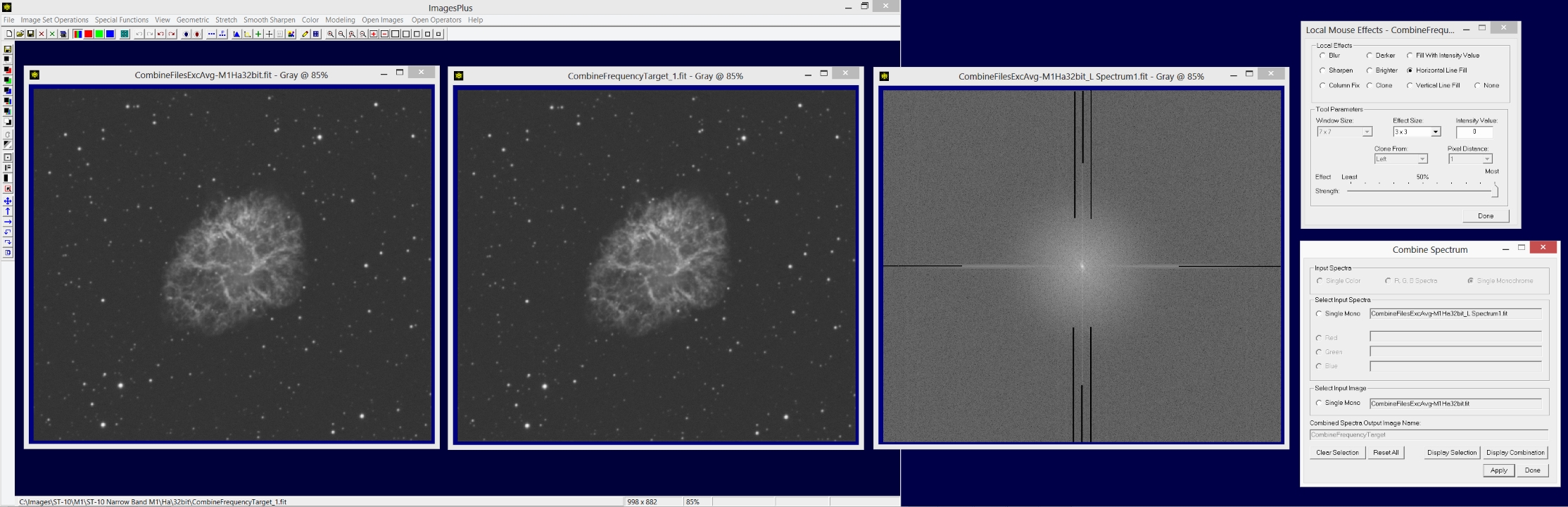 |
Use the Zoom 400% button on the top horizontal toolbar to zoom the initial and combination M1 image. Check the top left corner of the combination image for ringing near the top and left side edge. Reduce the length of the black painted horizontal and vertical lines to remove ringing if present. Press the Apply button on Combine Frequency to update the combination image using the current painted spectrum. The undo toolbar button can be used to remove unwanted paint strokes.
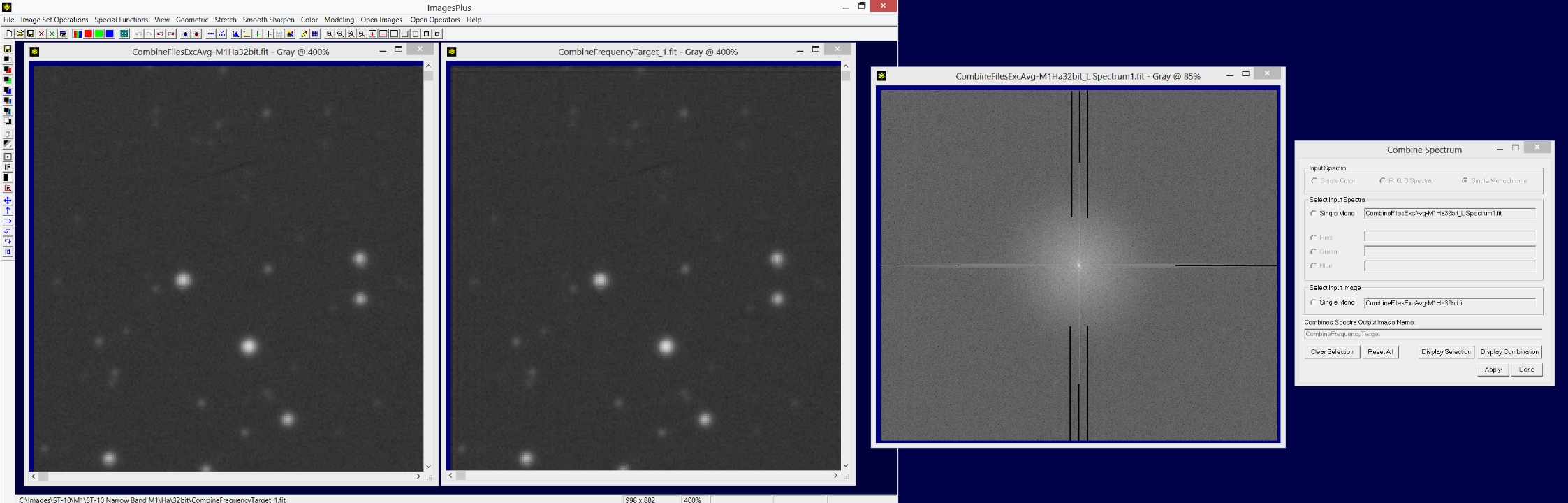 |
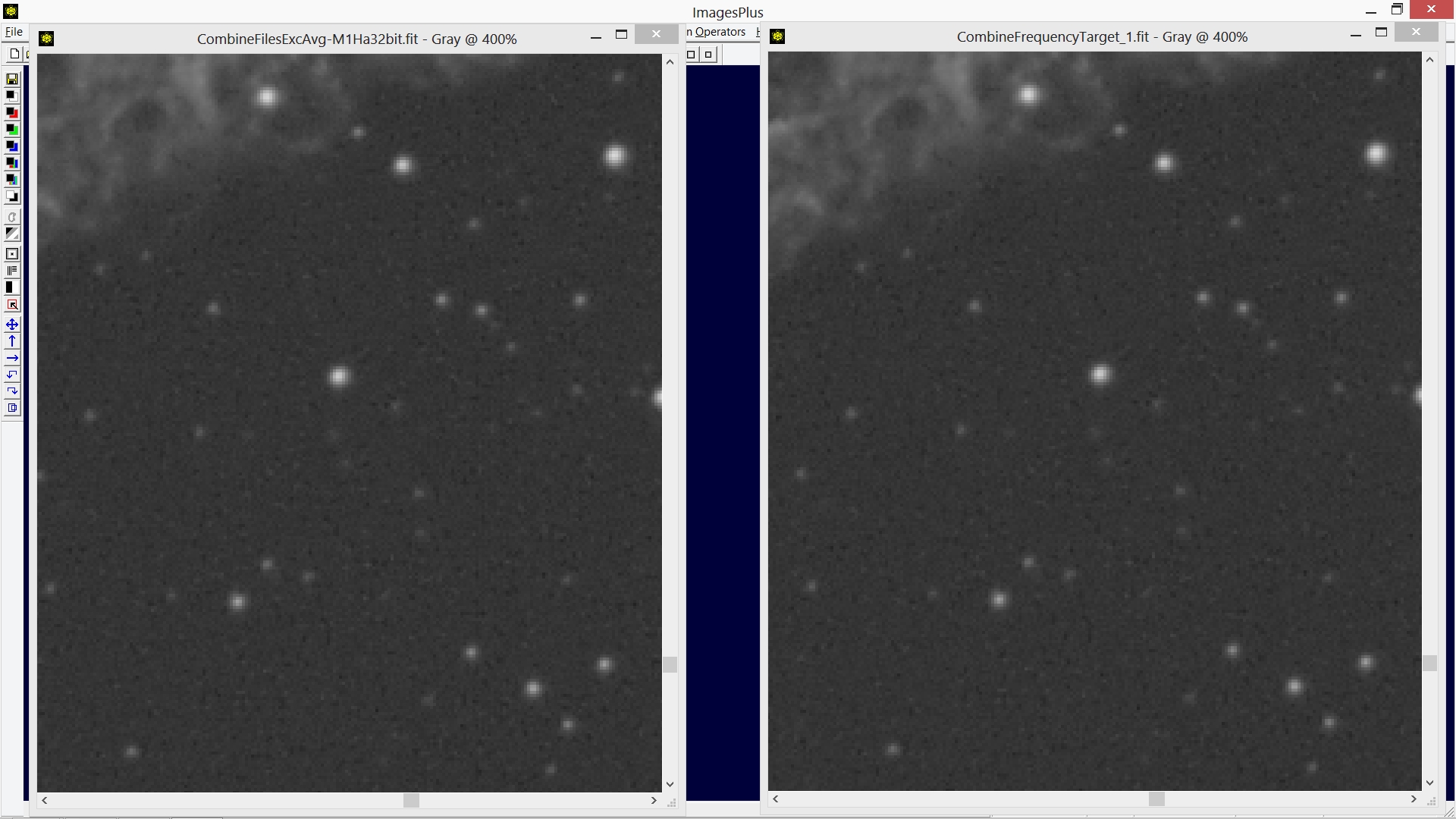
Inspect other parts of the combination image with zoom 400%. The calibrated, stacked and digital development image shown on the left has a fine pattern of short vertical and horizontal lines in its background. The combination image on the right was built with the painted spectrum with structured noise removed and has no fine vertical and horizontal line patter. Removing the fine structured noise improves processing that follows.
 |
On the left is the calibrated, stacked, and DDP stretched image with no structured noise removed and 10 iterations of adaptive Richardson-Lucy deconvolution applied. Deconvolution amplifies the fine vertical and horizontal structured noise line patterns. Removing structured noise reduces the vertical and horizontal line patterns from the stretched image and improves deconvolution sharpening as shown by the image on the right.
 |
Copyright © 2013 MLUnsold Digital Imaging. All Rights Reserved.