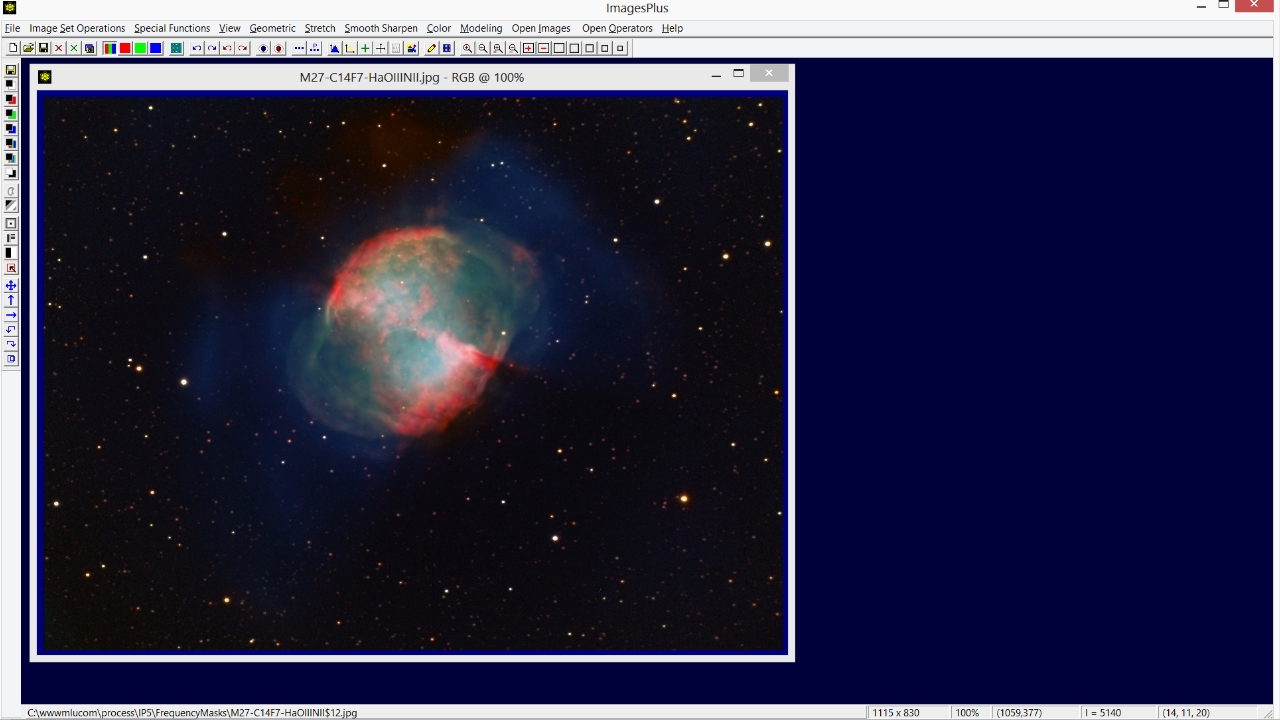
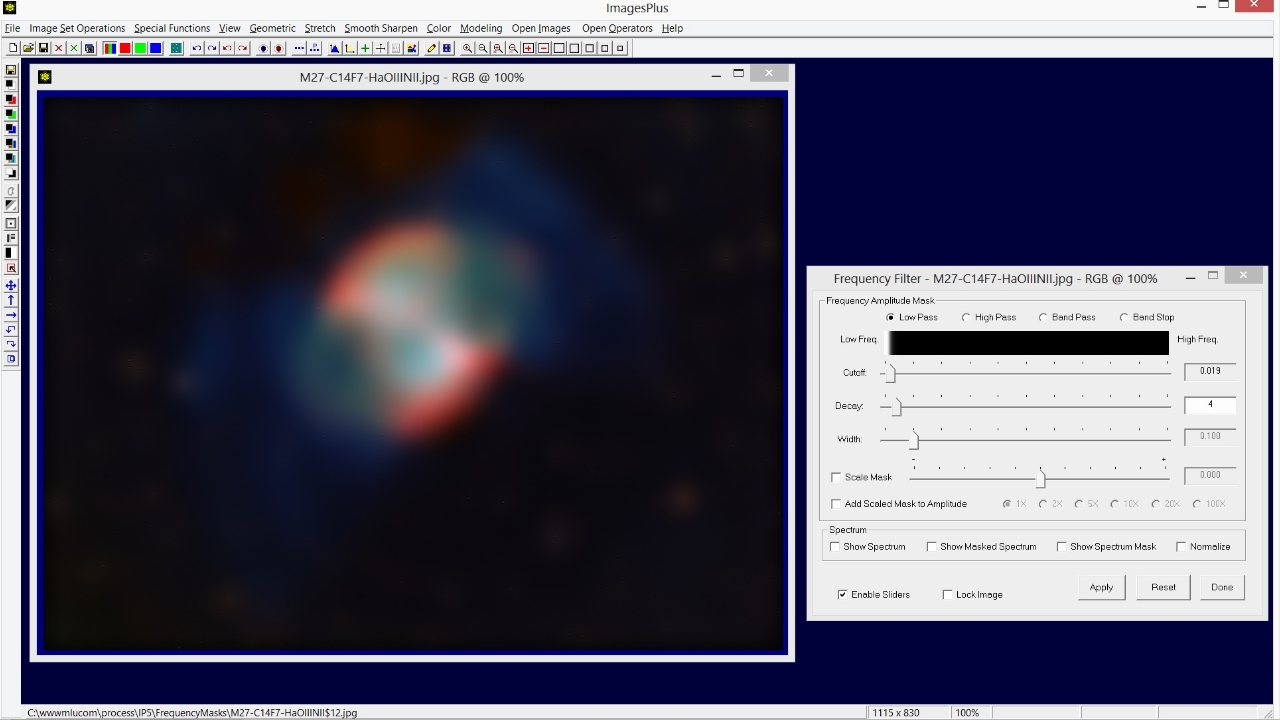
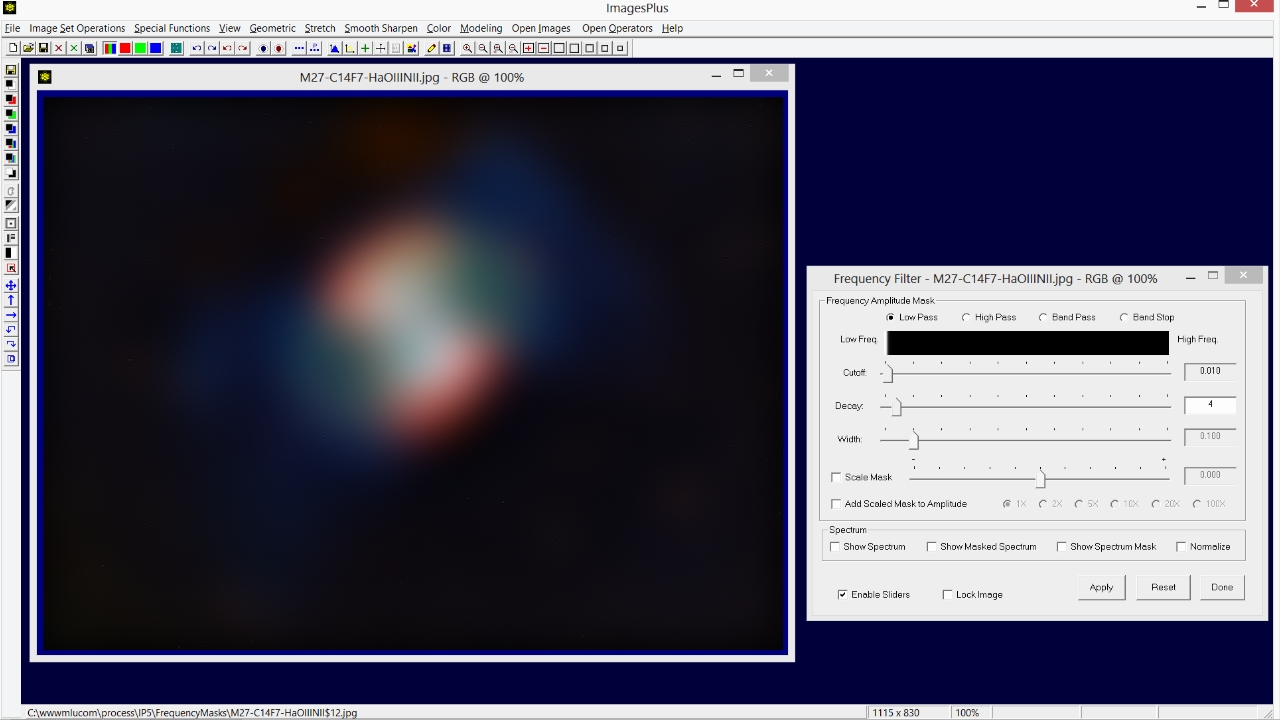
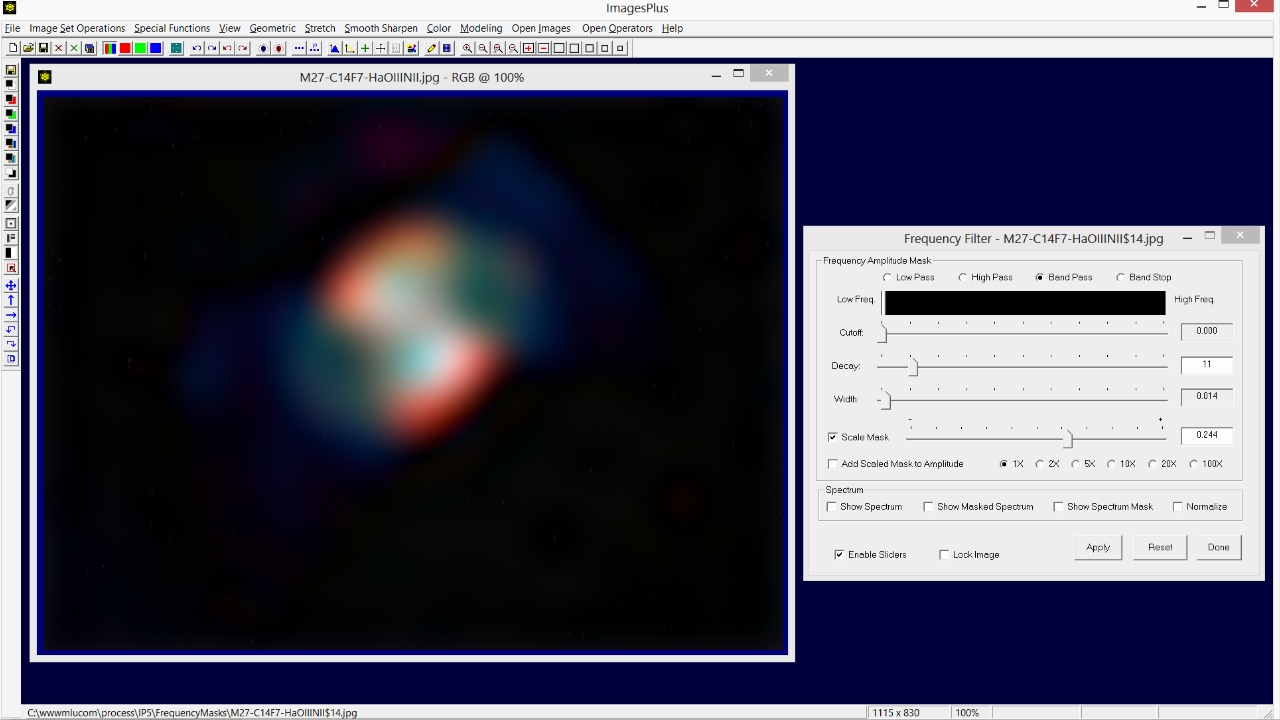
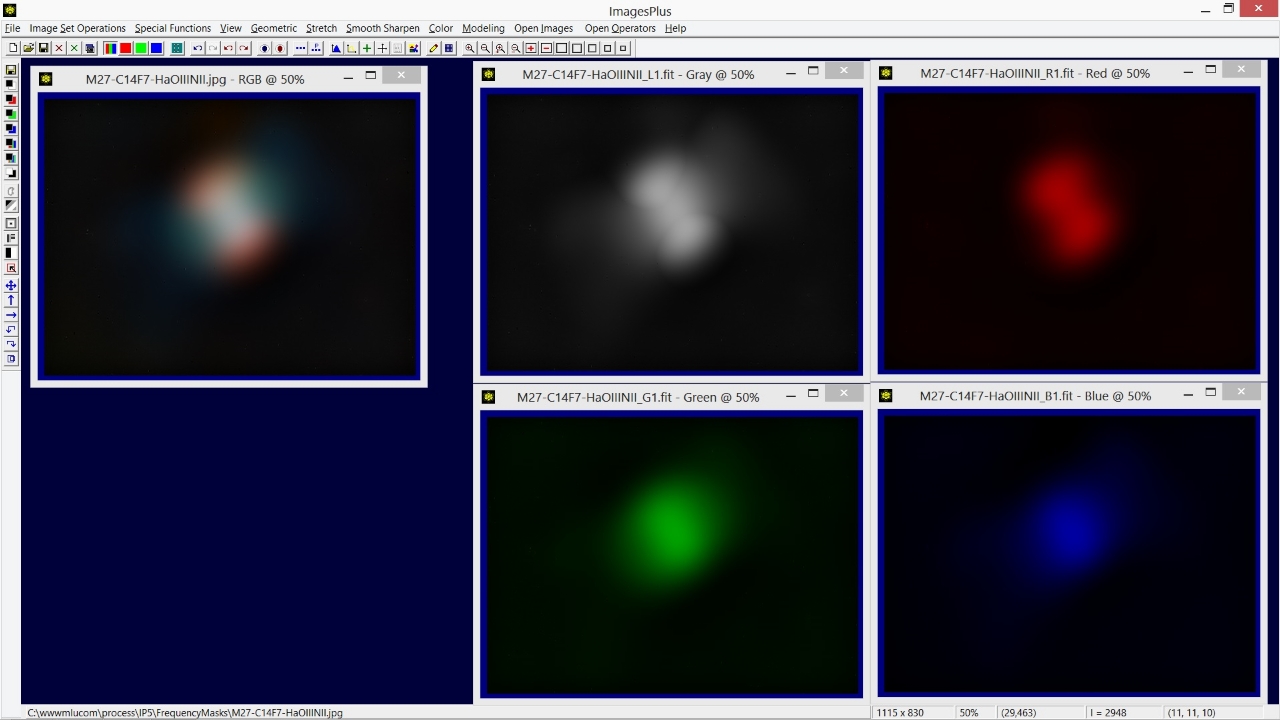
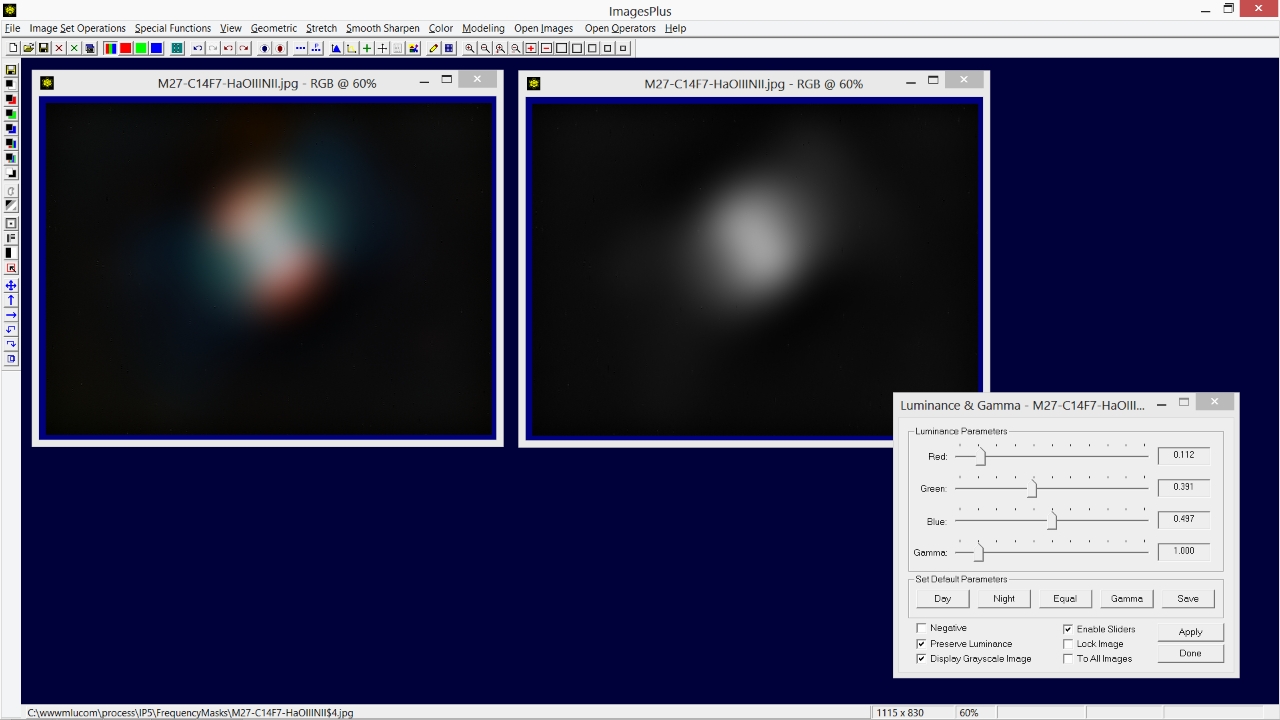
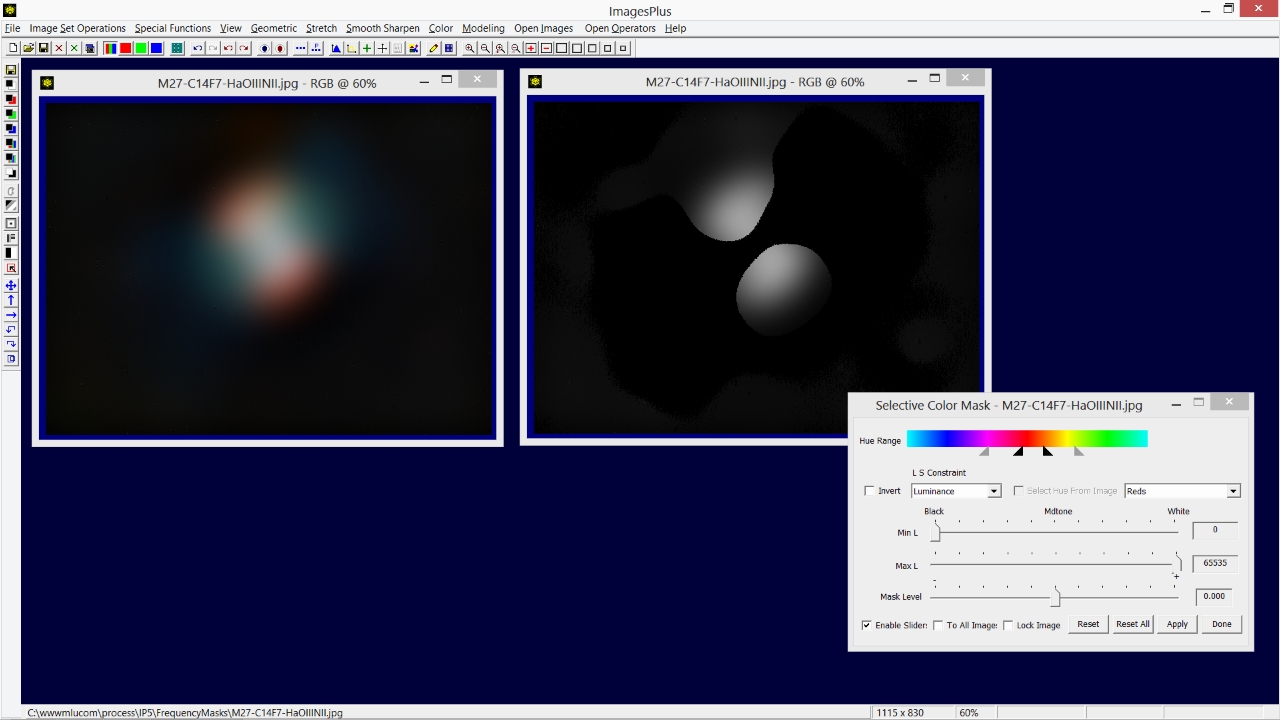
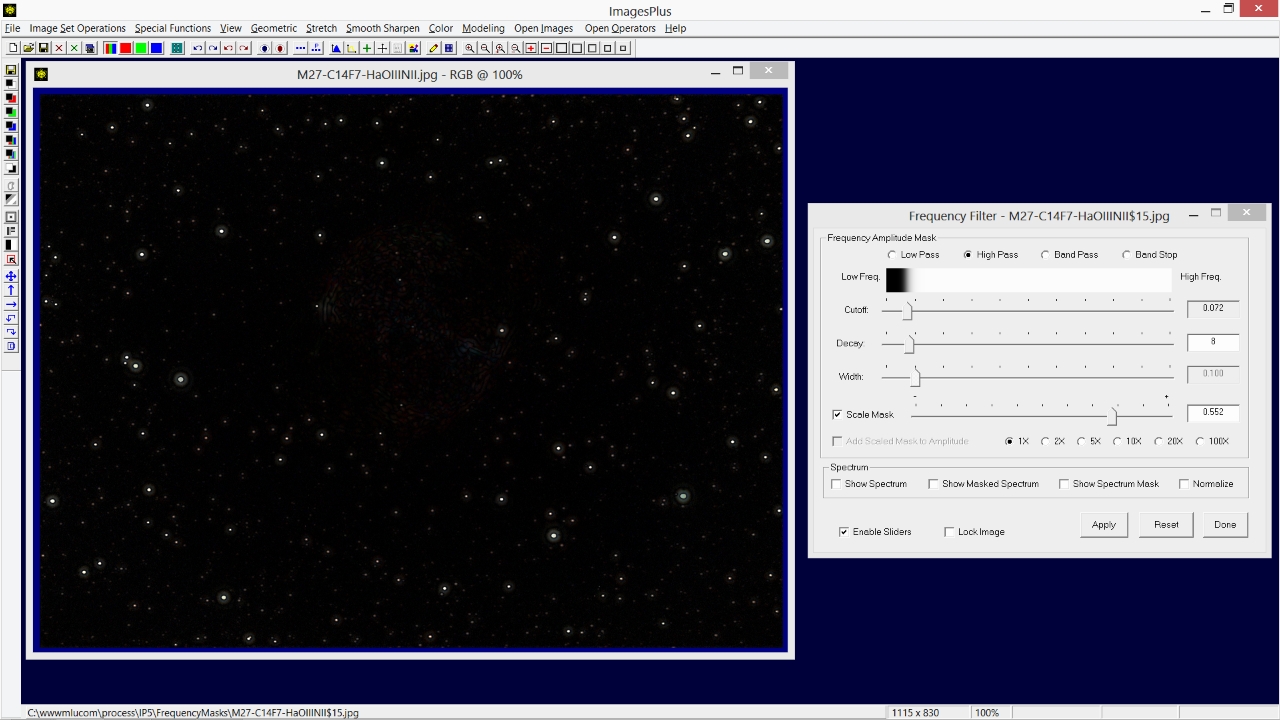
The Frequency Filter | High Pass option is used to keep only the high frequency stars and reject the low frequencies of M27. So Cutoff is set at a value of 0.072 and Decay is set at 8 to produce a sharp frequency cutoff. Note that large objects like M27 are removed but smaller objects like stars remain. Use the Scale Mask option on the Frequency Filter to adjust overall brightness.
 |
Special Functions | Pixel Math can be used to remove detail from the dark background that remains. On Pixel Math set the min, max, and feather range values to include only the dark background then use the multiply or subtract option to reduce brightness.
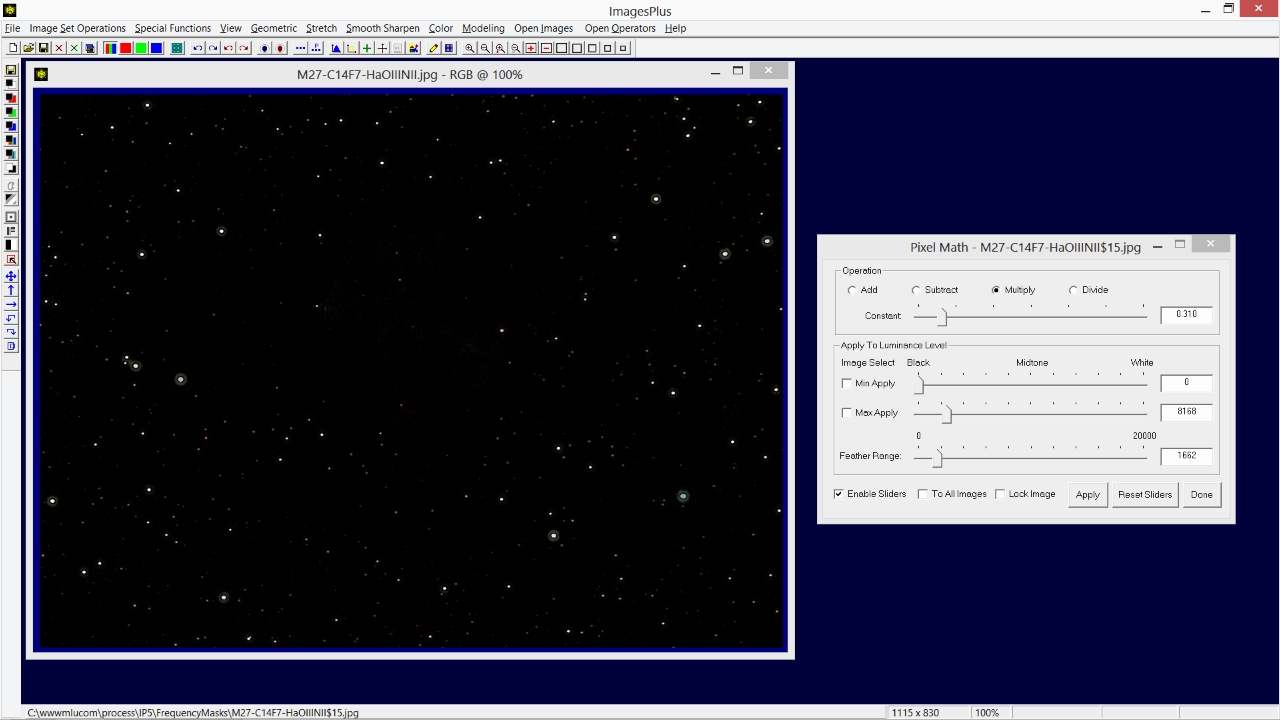 |
Haloes around brighter stars are removed by adjusting the min, max, and feather range sliders.
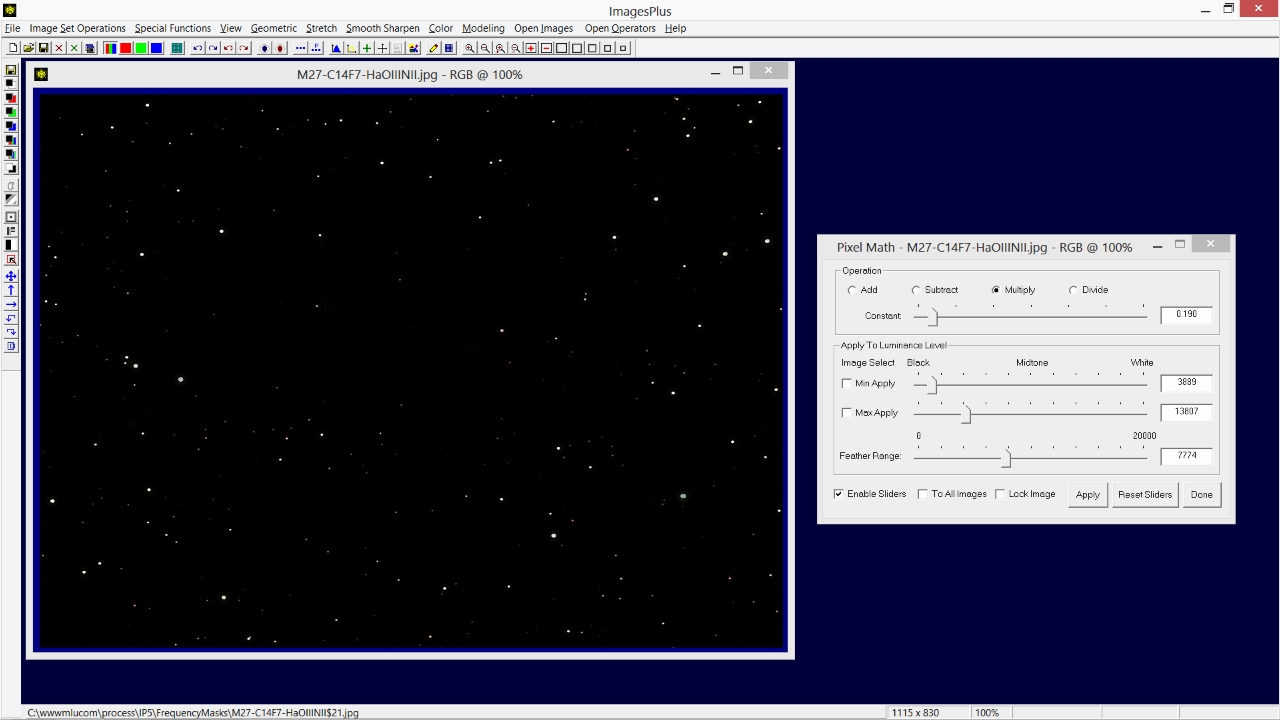 |
Copyright © 2013 MLUnsold Digital Imaging. All Rights Reserved.