- Digital Development is divided into four groups. The HDR Pre-Stretch Scale controls are used to map the image to different parts of the digital development stretch curve. Mapping the image data to different parts of the stretch curve allows great control over the brighness and contrast of the stretch applied to the background, midtones, and highlights. The DDP Stretch control group is used to control the shape of the stretch function and also background brightness and contrast. The Decompress Color controls are used to maintain star color that is compressed by aggressive stretch functions. The Sharpening controls provide an optional increase in sharpeness and are not used in this example.
- ArcSinH and digital development stretch tools both have the same color decompression and HDR pre-stretch scale functions. ArcsinH uses a different stretch curve than digital development and may perform better on some images.
- A set of 17 x 10 minute light frames, 10 flat, 10 dark, and 10 bias frames of M13 were collected using a 203mm F9 TMB reduced to F7 with a Canon 5D MII. After calibration the light frames were normalized, aligned, and stacked with excluded min max average using the methods described by DSLR Automatic Image Set Processing or CCD Automatic Image Set Processing.
- The stacked image of M13 is very dark and shown below. The goal is to brighten or stretch the image of M13 so that the faint outer stars are shown and the bright core is not over stretched. Star color is also increased.
- Color deompression is used directly with the stacked color image from a DSLR or one shot color CCD. To use color decompression with red, green, and blue stacked components from a monochrome CCD build a color RGB image from the components. Apply digital development with color decompression to the RGB image then add the luminance layer on top. See the tutorial that covers multiple luminance layers for layering details.
Initial very dark stacked color image of M13. The dark background will be stretched to show faint outer stars without over stretching the bright core. Star color will be increased.
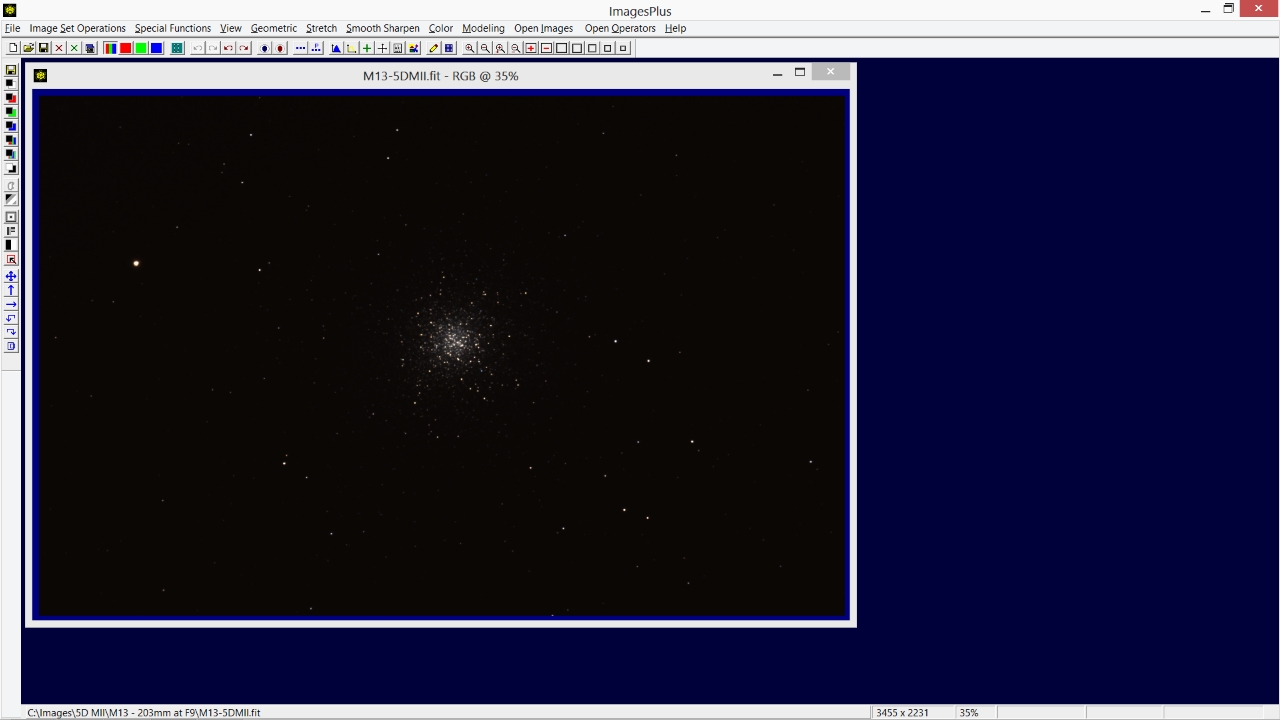 |
Step 1
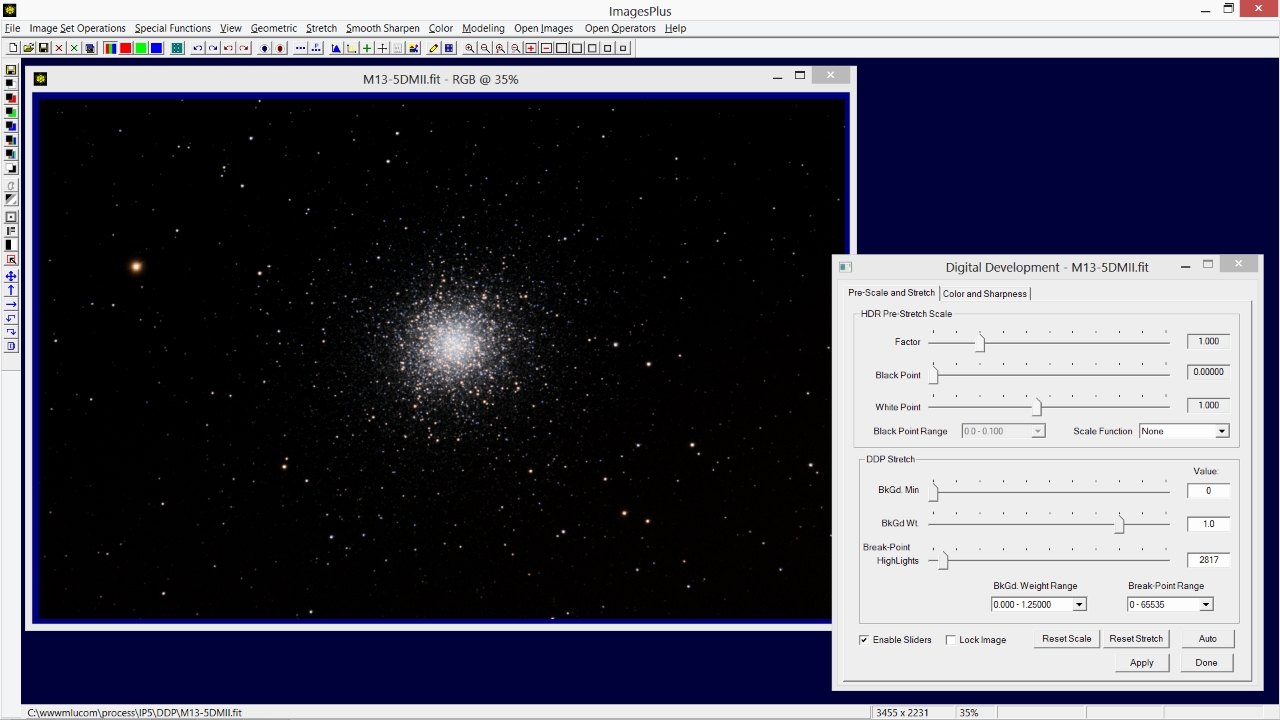
- The Stretch | Digital Development function is used to increase brightness and contrast of the dark background without over stretching the bright core of M13.
- First move the Break-Point Highlight slider to the left until the bright core looks properly stretched. At this point only focus on the bright core.
Break-Point Highlight is set to 2817. If the Break-Point slider is too sensitive for a given image then use the Break-Point Range list to adjust slider sensitivity to match the image.
 |
Step 2
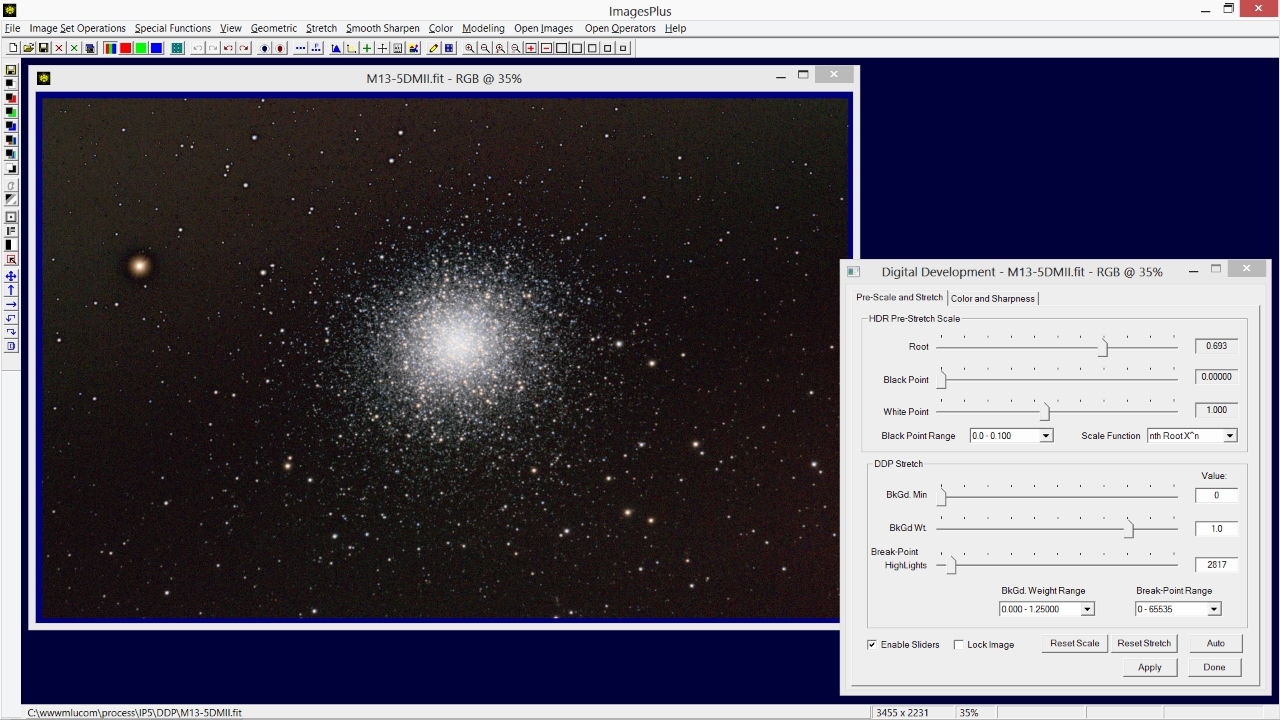
- The controls in the HDR Pre-Stretch Scale group will be used next to increase the stretch applied to M13 and the background stars. A linear pre-stretch scale could be used but both the background and core would be be increased in brightness. The faint outer stars of M13 require much more of a stretch than the core so a Nth Root pre-stretch scale is used to boost the outer area of M13 and maintain the core stars. Color is compressed by the aggressive stretch. Step 4 below will show how to decompress color.
Nth Root pre-stretch scale is used with Root = 0.693. As a result background star brightness is increased with an increase of contrast. Very little additional stretch is applied to the core of M13.
 |
Step 3
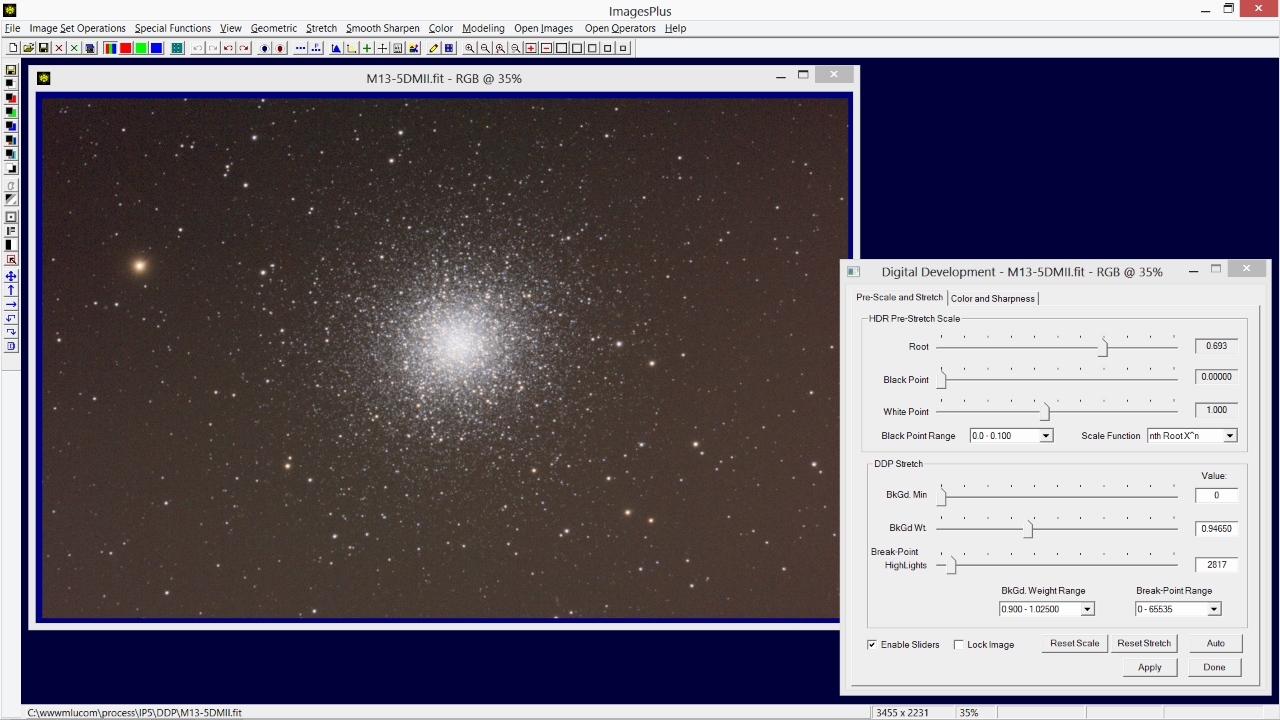
- Next adjust the Background Weight slider in the DDP Stretch control group to the left to even the background all the way to the image edge.
The Background Weight slider has been moved to the left to 0.94650 to even the background. If the slider is too sensitive use the Background Weight Range list box to adjust the slider sensitivity to match the image. The stretch will be adjusted to show faint outer stars and color.
 |
Step 4
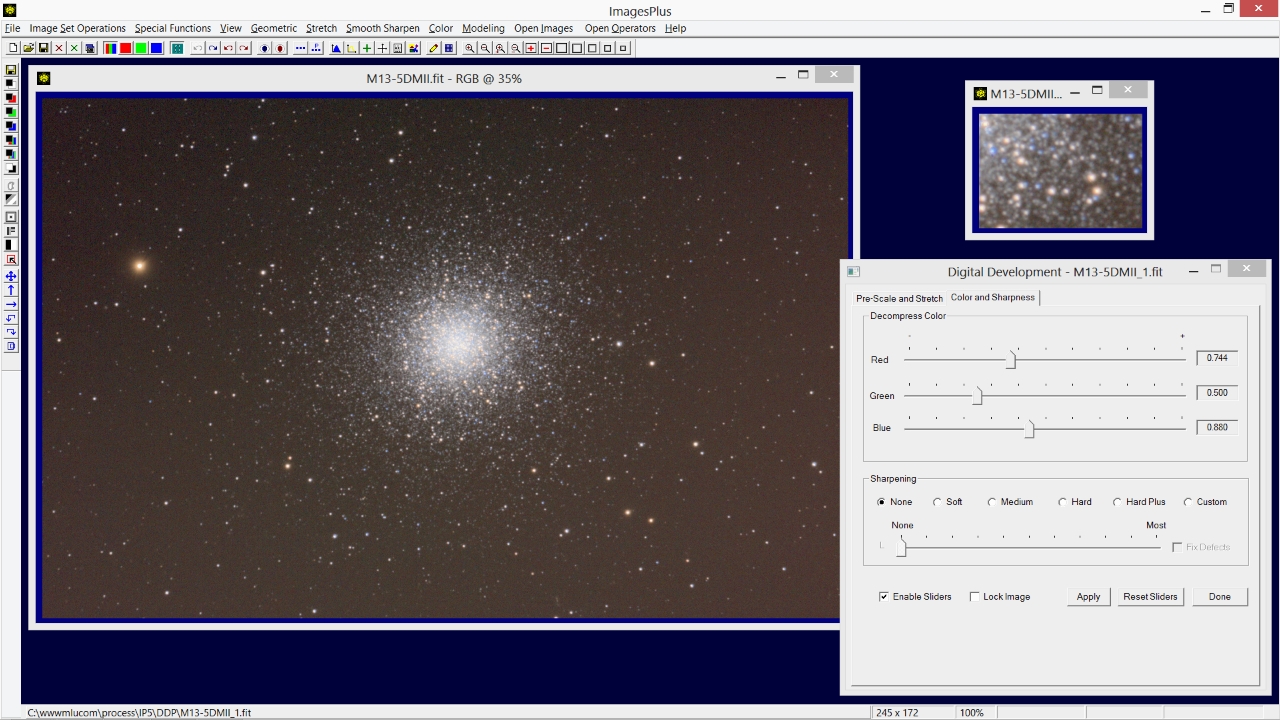
- The Decompress Color controls are used next to counter color compression from the aggressive digital development stretch.
Color decompression preserves color present in the initial stacked image and does not add new color. Red and blue are enhanced by moving their sliders to the right since red and blue are the dominate colors in this image of M13. The green slider has little effect since the M13 image has very little green. Adjust the red, green, and blue sliders to get good color without artifacts. Check the color adjustment using a full resolution crop.
 |
Step 5
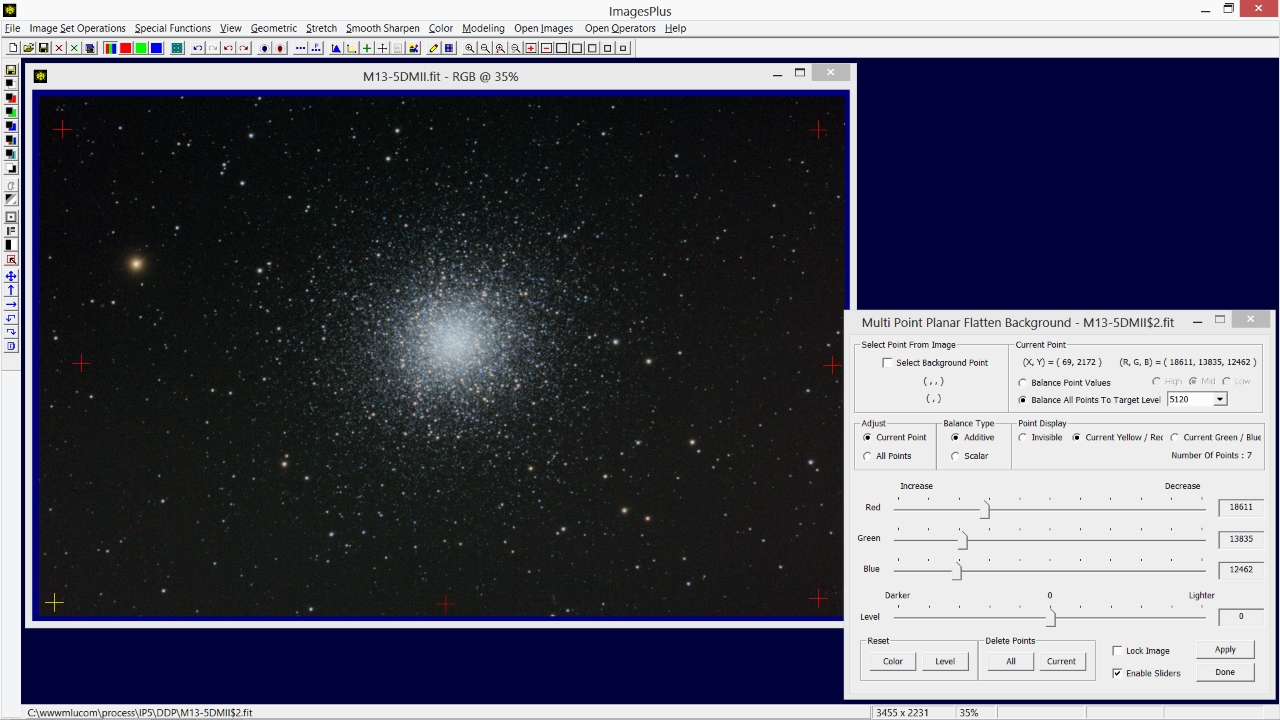
- The Special Functions | Multi-Point Flatten tool is used to color balance, flatten, and set the red background to dark gray.
Check the Select Background Point box then left-click on the image to select several background points. The color near each point is balanced. To automatically flatten each color balanced point to the same level select the Balance All Points To Target Level option. The default target level is dark gray or 5120 on a 16 bit scale. Color balance and level of each adjustment point can also be adjusted manually using the red, green, blue, and level sliders.
 |
Step 6
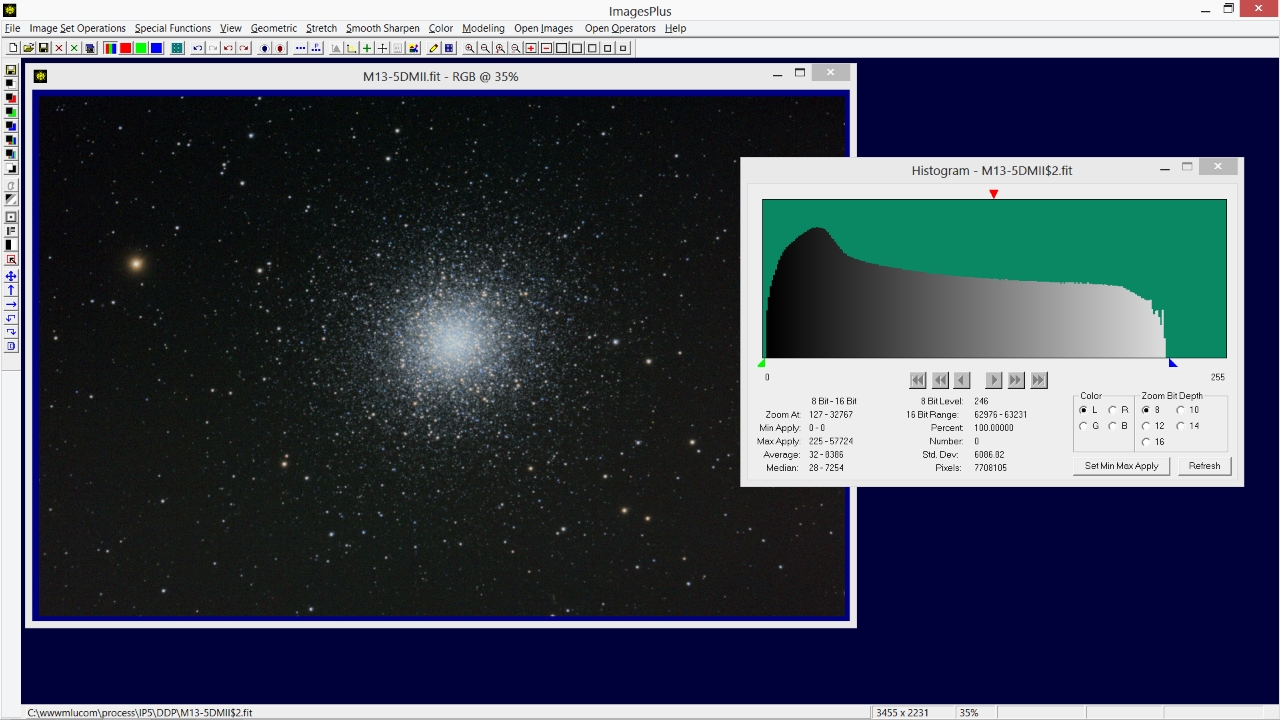
- The Modeling | Histogram tool is used to inspect pixel distribution after digital development and flatten.
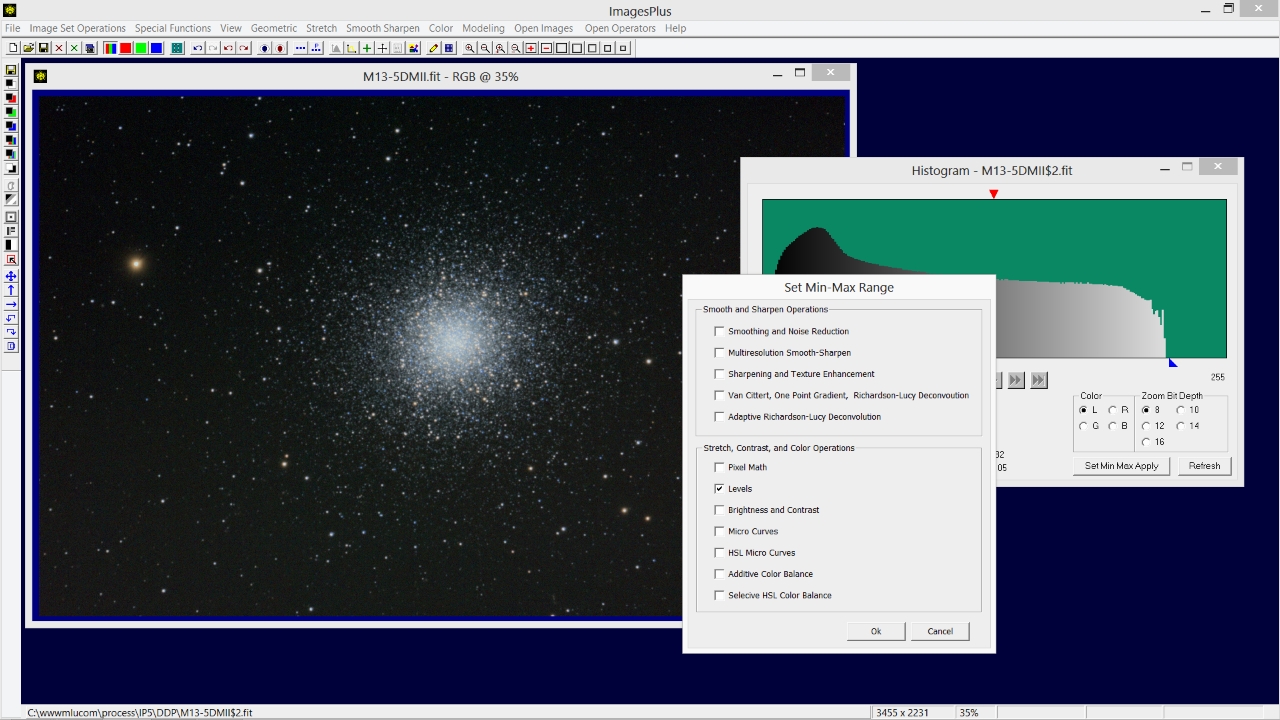
The right side of the histogram does not extend to 255 white. To set the white point blue triangle right-click under the histogram at its right edge. Press the Set Min Max Apply button to open the tool selection window.
 |
Check Levels then press Ok.
 |
Step 7
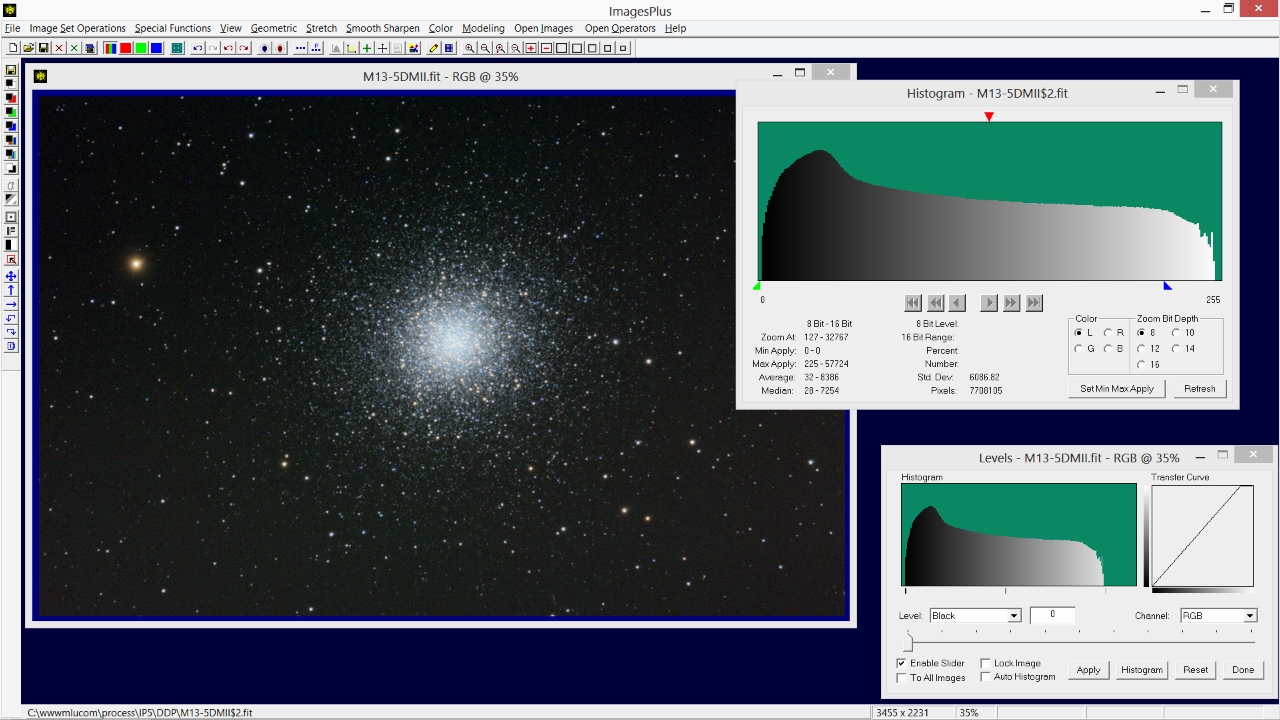
- The Stretch | Levels tool is opened and set to the white point selected on the histogram in the previous step.
Press Apply on the Levels tool to correct the white point. The histogram now extends from left black = 0 to white = 255.
 |
Step 8
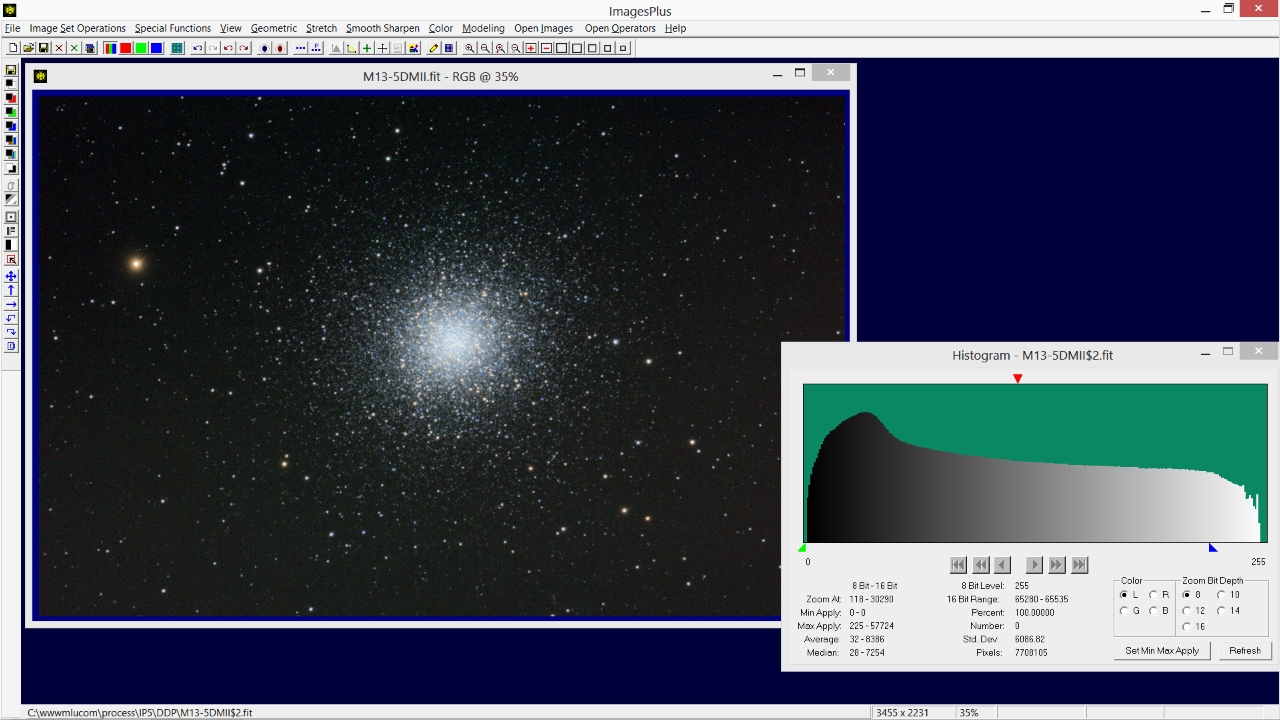
- The Histogram tool is used to check for clipped black and white.
Move the mouse pointer over the histogram near its right edge and notice the number of pixels at levels near white. This histogram shows the white level 255 to have 0 pixels so white is not clipped.
 |
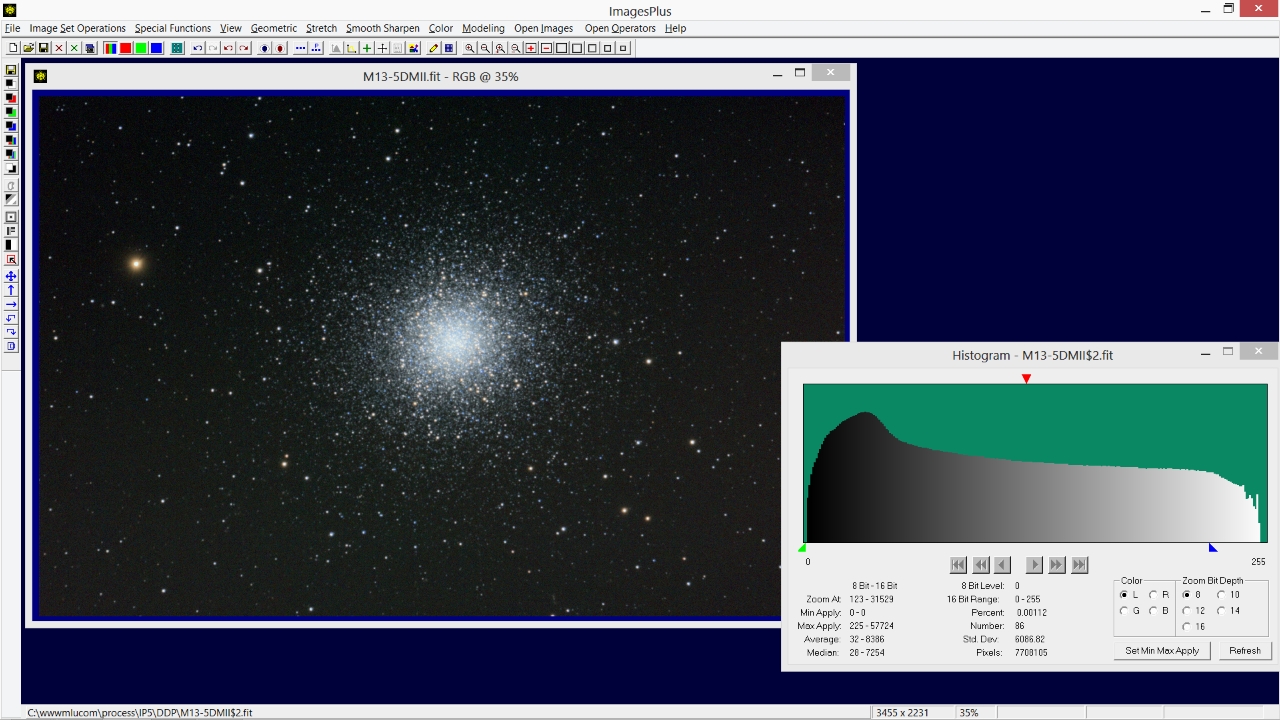
Move the mouse pointer over the histogram near its left edge and notice the number of pixels at levels near black. This histogram shows the 8 bit black level 0 to have 86 pixels. Since the M13 image is 16 bit the histogram needs to be set to 16 bit display to get the 16 bit pixel count at black = 0.
 |
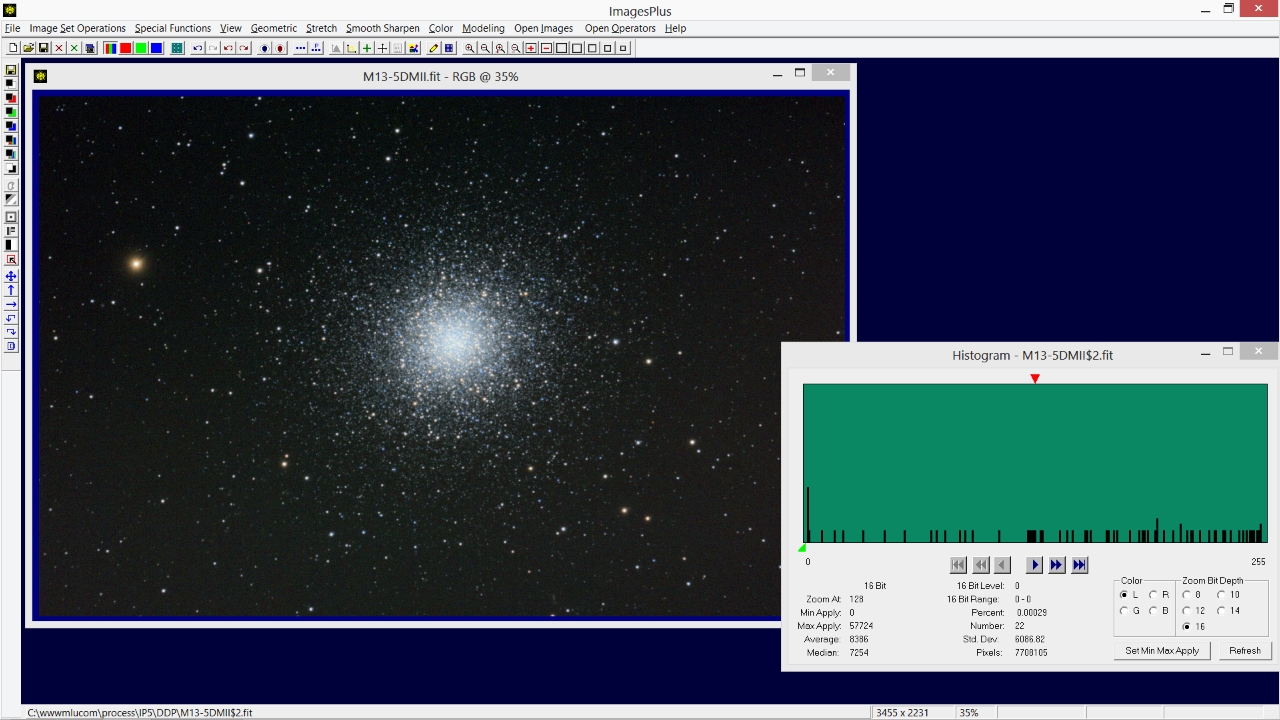
On the Histogram tool set Zoom Bit Depth to 16 then press the << button to set the 16 bit histogram to its far left side. The histogram now displays black = 0 to black = 255 from left to right on a 16 bit scale. Move the mouse pointer over the histogram near its left edge and notice the number of pixels at levels near black = 0. This histogram shows the 16 bit black level 0 to have only 22 pixels so black is not clipped.
 |
Processing Step Summary
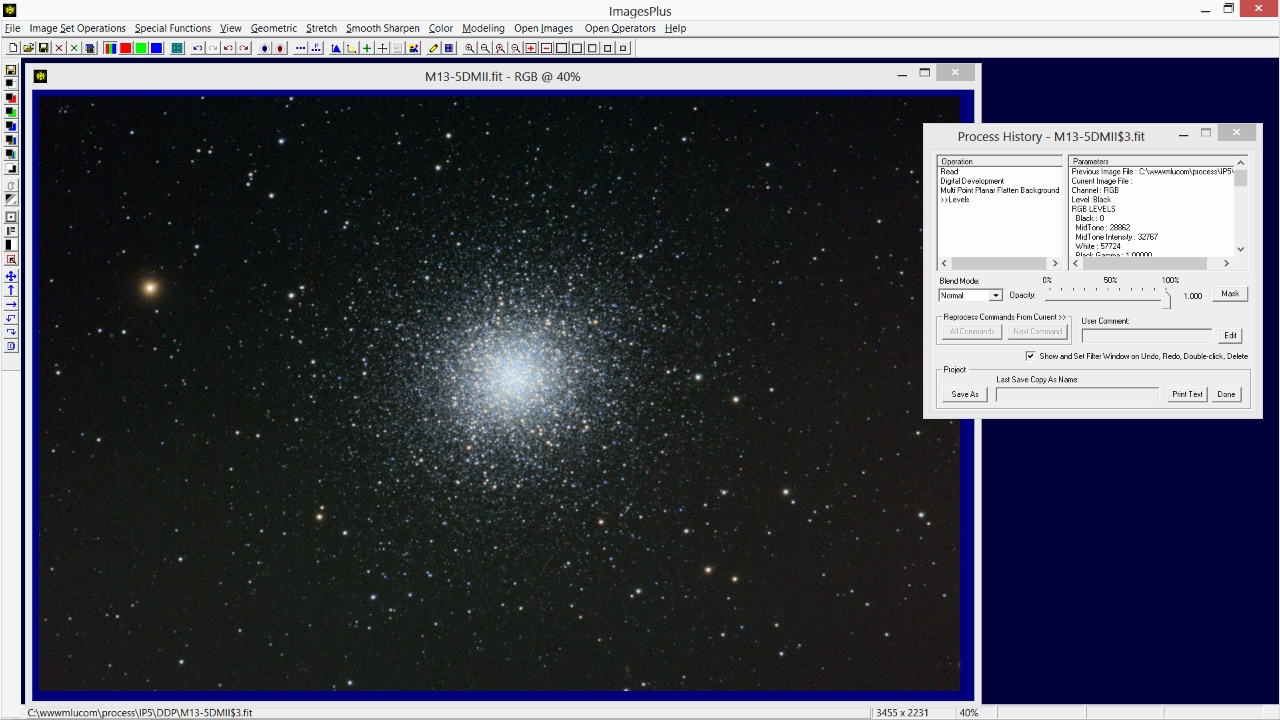
- The Process History window tracks filters applied to an image.
M13 with Process History window showing digital development, multi-point flatten, and levels applied to M13.
 |
Final digital development stretched image with color decompression ready for background smoothing, deconvolution, and fine color adjustment.
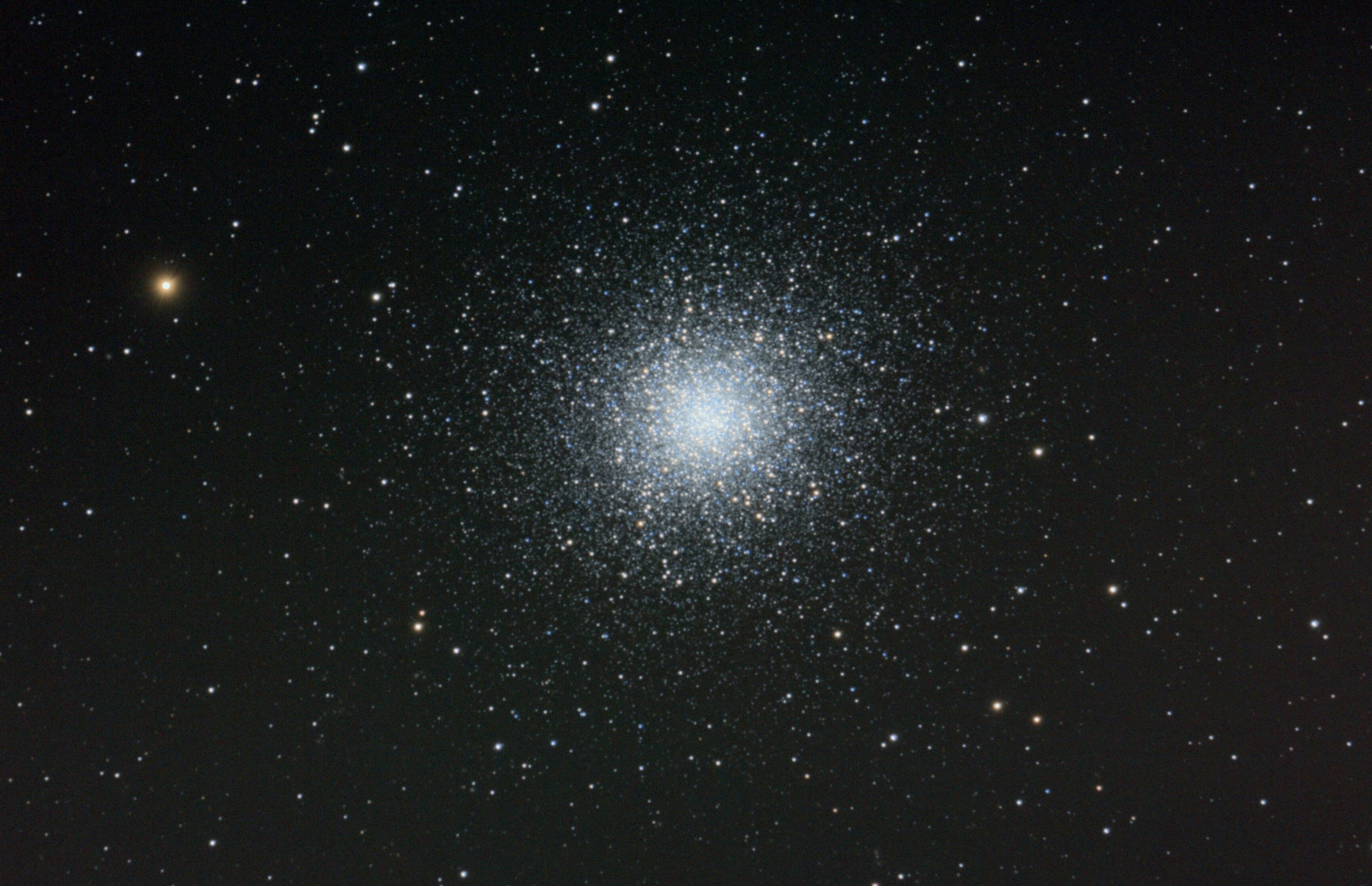 |
Copyright © 2013 MLUnsold Digital Imaging. All Rights Reserved.














